Sun Protection Strategies: Integrating Sunscreen into Everyday Life
Everyday sun protection is a simple, high-impact step in skin care that supports hydration, barrier health, and long-term skin condition. This brief overview highlights practical ways to make sunscreen part of morning and daytime routines without disrupting cleansing, moisturizing, or other treatment steps.
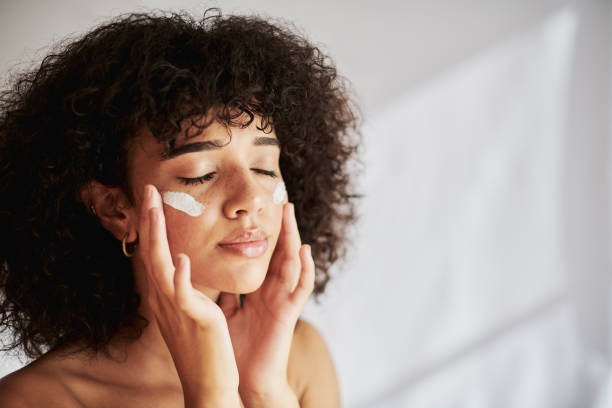

Daily sun protection is foundational to a balanced skincare approach and supports hydration, barrier resilience, and antiaging goals. Integrating sunscreen into everyday life means treating it as a nonnegotiable step—like cleansing and moisturizing—so that UV protection becomes automatic rather than optional. Small adjustments—timing, texture choice, and layering—help make sunscreen comfortable for sensitive skin and compatible with ingredients such as ceramides and hyaluronic acid.
This article is for informational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Please consult a qualified healthcare professional for personalized guidance and treatment.
How does sunscreen fit into a daily routine?
Sunscreen is most effective when applied consistently as the last step of a morning skincare routine, after moisturizer and any lightweight treatments. For most people the sequence is cleansing, serums or treatments, moisturizer, then sunscreen. If makeup follows, allow sunscreen to set for a minute before applying foundation. Reapply sunscreen every two hours when outdoors, and sooner after swimming or heavy sweating. Treating sunscreen as routine helps normalize application and reduces missed spots.
How do cleansing and moisturizer support the skin barrier?
Cleansing should remove impurities without stripping natural oils that maintain the barrier. Choose gentle cleansers that respect the microbiome and avoid over-exfoliating in the morning. A moisturizer with ceramides helps restore lipids in the stratum corneum and improves barrier function, which can reduce sensitivity to environmental stressors. When layering, allow cleansing and moisturizer time to absorb—this improves sunscreen adherence and avoids pilling that undermines protection.
What role do hydration, hyaluronic, and ceramides play?
Hydration is essential for skin comfort and resilience. Hyaluronic acid provides immediate hydration by attracting water, while ceramides help lock moisture into the barrier. Using hydrating serums followed by a ceramide-containing moisturizer creates a strong base that sunscreen can sit on without compromising efficacy. For drier or mature skin, richer hydrating steps can also enhance the cosmetic feel of sunscreen and support antiaging goals by reducing transepidermal water loss.
How can sunscreen choices address microbiome and sensitivity?
Sunscreen formulations vary: mineral (physical) filters like zinc oxide or titanium dioxide sit on the surface and are often well-tolerated by sensitive skin, while chemical filters absorb UV energy and may suit other skin types. Look for non-irritating, fragrance-free options if microbiome balance or sensitivity is a concern. Patch testing new products and introducing one product at a time helps identify reactions. Supporting the microbiome with gentle cleansing and balanced moisturization reduces the risk of irritation from new topical products.
How does sustainability influence sunscreen selection?
Sustainability considerations include packaging recyclability, reef-safe formulations, and ingredient sourcing. Mineral sunscreens are often marketed as reef-friendly, but environmental impact assessments depend on formulation and local regulations. Choose products with transparent ingredient lists and sustainable packaging where possible. Balancing sustainability with efficacy and skin compatibility matters: prioritize consistent sun protection first, then look for brands that align with environmental values without compromising SPF performance.
What are the antiaging benefits of consistent sun protection?
Regular sunscreen use reduces cumulative UV exposure, a primary driver of photoaging such as fine lines, pigmentation, and loss of elasticity. Integrating sunscreen into daily life complements other antiaging measures—hydration, ceramide-supporting moisturizers, and topical antioxidants—by preventing new UV-related damage. Over time, consistent protection helps maintain more even skin tone and reduces the need for corrective procedures. Pairing sunscreen with a comprehensive routine supports both immediate comfort and long-term skin health.
Conclusion Making sunscreen a habitual part of everyday skincare supports hydration, barrier integrity, and antiaging aims while protecting against UV-related damage. By aligning sunscreen choice and application with cleansing, moisturizing, and treatment steps—and considering sensitivity, the microbiome, and sustainability—you can build a practical, comfortable daily routine that preserves skin health.