Using analytics to cut waste and improve throughput
Analytics drives measurable improvements across production and supply processes by turning operational data into actionable insight. This article explains practical ways analytics reduces waste, raises throughput, and supports sustainability and compliance in modern manufacturing and logistics.
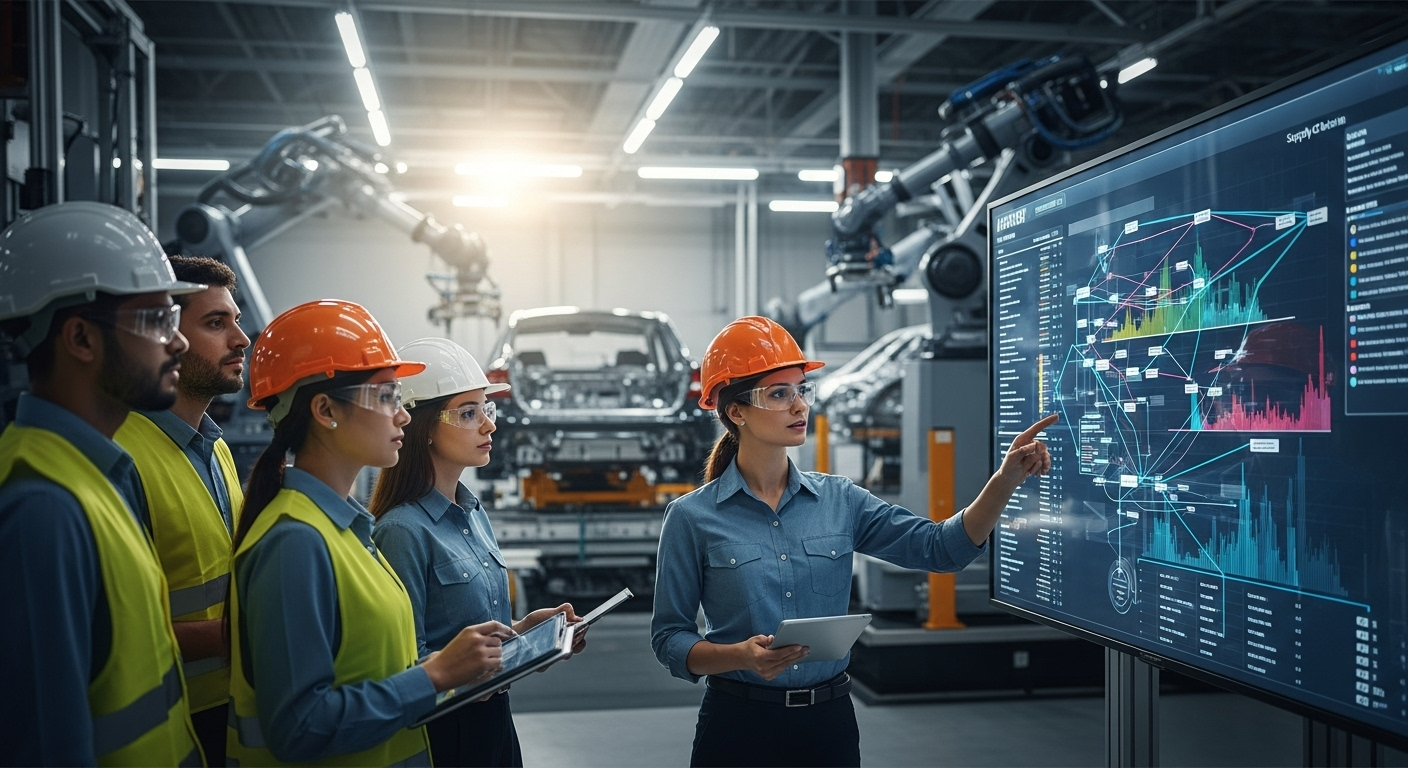

Analytics is reshaping how organizations identify and eliminate sources of waste while increasing throughput across production lines and support functions. By combining data from machines, inventory systems, and logistics flows, analytics helps teams pinpoint bottlenecks, measure cycle times, and prioritize interventions. Practical deployments rely on clearly defined KPIs, consistent data collection, and iterative testing: small, repeatable improvements compound into sustained gains in efficiency and reduced material and time waste.
How analytics improves manufacturing efficiency
In manufacturing environments, analytics provides visibility into cycle times, yield rates, and work-in-process inventory. Statistical process control and real-time dashboards let engineers spot deviations from expected performance quickly, reducing scrap and rework. Root-cause analysis driven by machine and process data highlights recurring defects and process drift, enabling targeted process changes. When combined with continuous improvement practices, analytics shifts decisions from reactive firefighting to data-guided adjustments that preserve throughput and improve overall equipment effectiveness (OEE).
What analytics mean for supply chain and logistics
Supply chain analytics links demand signals, inventory levels, and transportation events to reduce stockouts and overstocks. Route optimization and demand forecasting shorten lead times and lower logistics costs while improving on-time fulfillment. Visibility into inbound and outbound flows reveals where delays erode throughput, and scenario modeling helps planners evaluate trade-offs between inventory buffers and faster replenishment. These insights support procurement decisions and align logistics with production cadence to smooth end-to-end flow.
Automation, robotics, and operations insights
Data from automation and robotics provides high-resolution metrics on cycle performance, downtime causes, and task variability. Analytics applied to this telemetry helps operations teams sequence tasks more effectively, balance lines, and detect inefficient handoffs between automated and manual work. Performance monitoring can expose underutilized assets or mismatched takt times, enabling adjustments in cell layouts or software configurations. When analytics informs control parameters, automation becomes easier to scale while maintaining stable throughput.
Predictive maintenance and maintenance planning
Predictive maintenance uses sensor data, historical failures, and analytics models to anticipate equipment degradation before it causes unplanned downtime. Condition monitoring for bearings, motors, and critical components identifies trends that warrant inspection or replacement during scheduled windows, protecting throughput. Integrating maintenance planning with production schedules and facilities constraints minimizes disruption. Analytics also helps prioritize maintenance tasks by criticality and failure risk, optimizing spare parts procurement and labor allocation.
Procurement, compliance, and cost control
Analytics supports procurement by quantifying supplier performance, lead-time variability, and cost drivers. Spend and supplier analytics reveal opportunities to consolidate purchases, standardize components, or negotiate terms that reduce variability in the supply chain. Compliance analytics tracks documentation, traceability, and process adherence to regulatory standards, reducing the risk of recalls or stoppages. Together, these views help control total cost of ownership and align procurement strategies with operational throughput goals.
Safety, sustainability, and facilities management
Operational analytics extends into safety and sustainability by correlating process parameters with incident reports, energy use, and waste streams. Facilities analytics highlights inefficient HVAC, lighting, or compressed-air systems that inflate costs and create variability. Waste reduction strategies informed by data can lower material consumption and emissions while preserving output. Safety analytics helps identify risky patterns in processes or shifts, allowing targeted training or engineering controls that keep operations running and compliant.
Data governance and cross-functional collaboration are crucial: analytics only improves throughput when data quality, ownership, and decision protocols are clear. Start with pilot projects focused on measurable KPIs, scale validated models, and build user-friendly dashboards that operational staff trust. Over time, routine monitoring and iterative adjustments convert one-off gains into persistent performance improvements.
Conclusion
Using analytics to cut waste and improve throughput relies on integrating diverse data sources, focusing on measurable KPIs, and coordinating actions across manufacturing, supply chain, maintenance, and facilities. When analytics is applied with clear governance and practical interventions, organizations can reduce material and time waste, raise throughput, and support safer, more sustainable operations.